Article • 5 min read
AI agent vs. AI chatbot: Key differences and features
AI agents and AI chatbots are two options that businesses can use to streamline operations and provide a better customer experience. Learn which one is better for you below.
Candace Marshall
Vice President, Product Marketing, AI and Automation
Last updated August 18, 2025
Customer service technology has come a long way since the days of endless hold music and “your call is very important to us.” Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) have revolutionised customer support processes, making them more efficient and intuitive. As businesses take advantage of these innovations, it’s important to distinguish between two popular AI-powered tools: AI agents vs. AI chatbots.
This breakdown of the differences between an AI agent and an AI chatbot will highlight how each tool works and where each one excels. Understanding these distinctions will help you make investments that better align with your customer service goals and drive more effective support.
More in this guide:
- What is an AI chatbot?
- What is an AI agent?
- Differences between an AI agent and an AI chatbot
- How to choose between an AI agent and an AI chatbot
- Frequently asked questions
- Invest in an industry-leading AI agent with Zendesk
What is an AI chatbot?
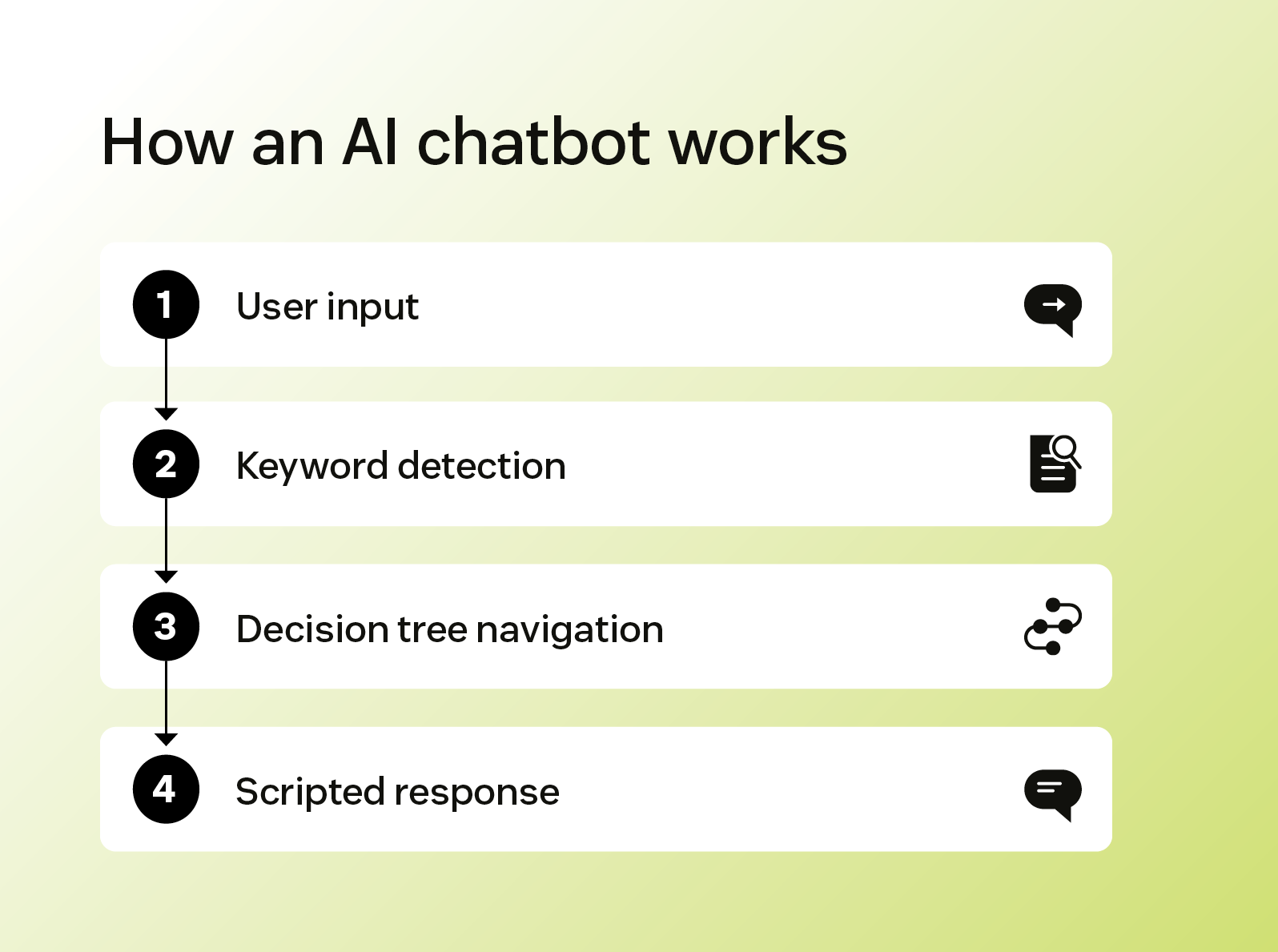
An AI chatbot is a tool that follows pre-defined rules to interact with customers. It’s programmed to recognise keywords in customer messages and respond with scripted answers that guide users through a limited set of interactions.
These systems rely on basic natural language processing (NLP) to identify common phrases and match them to pre-built responses. As a result, they can’t personalise responses beyond what’s explicitly programmed.
AI chatbot use cases
AI chatbots are beneficial primarily for managing repetitive tasks that follow rule-based patterns. They can provide automated support for common enquiries, streamlining the customer experience.
Some typical use cases include:
- Customer FAQs: Answering common questions about things like shop hours, return policies, or account settings
- Scheduling: Guiding users through booking an appointment or a reservation
- Basic troubleshooting: Walking customers through step-by-step solutions for known issues
- Check order status: Accessing real-time updates from back-end systems to share shipping details or delivery timelines
One recognisable example is Domino’s pizza-ordering chatbot, “Dom,” which allows customers to place an order and track it in real time. It’s a simple way to keep customers informed without contacting support.
What is an AI agent?
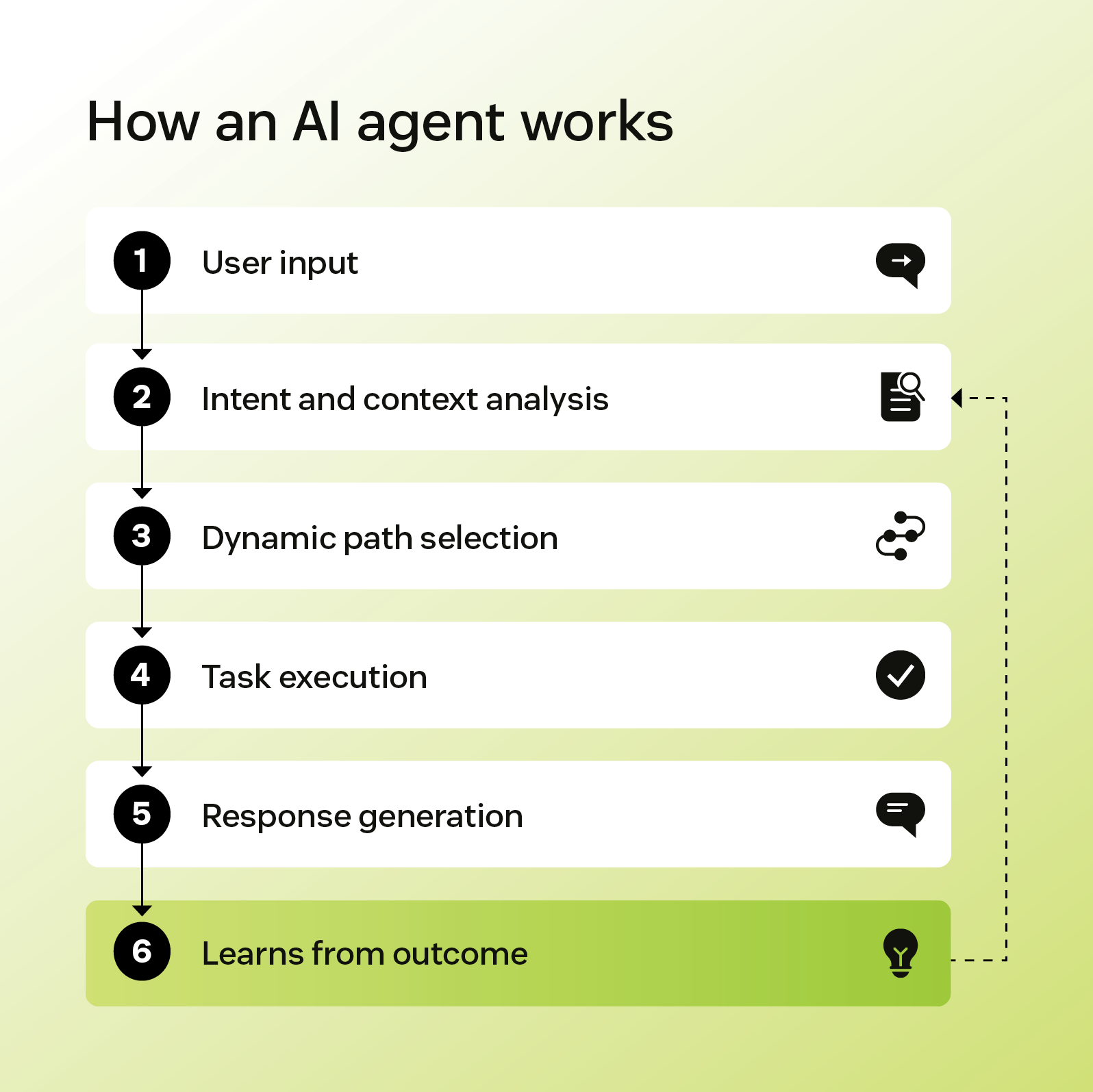
An AI agent is an autonomous programme that analyses conversations and makes context-based decisions. Unlike chatbots, which follow set rules, agents can independently assess a situation, determine the best course of action, and execute it.
AI agents are built on large language models (LLMs), which allow them to interpret nuance and adapt their behaviour over time. They can also connect to external tools like customer relationship management (CRM) systems, giving them information they can use to further personalise responses or complete tasks on behalf of a user.
AI agent use cases
Since AI agents can accomplish tasks independently, they are primarily used to help solve more complex customer problems.
Some specific use cases include:
- Advanced autonomous resolution: Resolving multi-step issues like billing disputes or rebooking a flight without human intervention
- Provide 24/7 support Helping customers receive consistent support regardless of the time zone
- Route tickets: Assessing conversations and routing requests to the right team or priority level
For example, UK-based stationery company Papier turned to Zendesk AI to support its expansion into the US. Now, the AI agent handles a large volume of requests after hours, helping reduce ticket backlogs and improving response times across the board.
Differences between an AI agent and an AI chatbot
While both AI agents and AI chatbots are integral to modern customer service, they differ significantly in how they understand and respond to customer needs. Let’s have a closer look at some of the key differences.
Customer service interactions
Because AI chatbots follow a script, interactions tend to feel more transactional. Customers are guided through a set path with limited flexibility, often having to rephrase or restart if their question doesn’t match the expected flow.
Meanwhile, interactions with AI agents feel more conversational and personalised. In some cases, agents can even detect potential problems before a customer gets in touch, enabling proactive support rather than just reactive responses. This leads to a more natural, satisfying experience for customers.

Quality assurance
Both AI agents and AI chatbots play a role in quality assurance (QA) by collecting data that sheds light on agent performance and customer satisfaction.
However, AI agents take QA further by analysing conversations in real time and picking up on subtleties like sentiment shifts and tone. They can also generate detailed insights and alert supervisors immediately, enabling quicker intervention and coaching.
AI chatbots, on the other hand, mainly assist with collecting structured feedback, such as satisfaction surveys or simple sentiment checks. This narrower view focuses on customer reactions rather than conversation dynamics.
Task complexity
AI chatbots are limited to handling simple tasks with fixed rules and predictable outcomes. Because they follow pre-defined paths, they struggle with anything that requires flexibility or judgement.
In contrast, AI agents are equipped to manage higher levels of complexity. They can handle multi-step workflows, respond to changing context mid-interaction, and make decisions based on real-time inputs. This makes them better equipped for resolving nuanced customer issues that chatbots can’t address with a single scripted response.
Scope of knowledge
Chatbots rely on pre-defined knowledge sources, so their scope of knowledge is limited to the content they were trained to reference, like help centre articles or scripted responses. If a question falls outside those boundaries, they typically can’t provide a useful response.
AI agents have a much broader scope of knowledge because they can access external systems and tools and use LLMs to synthesise relevant information on the fly. This is especially valuable in industries like retail, where AI can access inventory systems or order histories to provide more relevant and accurate responses.
Learning and adaptability
Chatbots are largely static, meaning they don’t adapt or improve independently. Any updates require manual retraining or rule updates by a human team. For instance, if a chatbot keeps receiving questions about a new product that is not in its training data, it won’t be able to respond until someone manually adds that information.
AI agents, by comparison, are built to learn from experience. They can retain context from past conversations and adjust behaviour based on new information. Even more impressively, they can learn from outcomes, gradually improving how they respond based on what has worked well in past interactions.
How to choose between an AI agent and an AI chatbot
As AI in customer service becomes more common, businesses are often faced with a decision: Do you need a simple tool to automate routine questions, or a more advanced solution to handle full conversations and actions autonomously?
The answer depends on your goals, resources, and the type of experience you want to deliver. Here are a few factors to consider:
- Determine your goals. If you're looking to automate straightforward interactions and speed up response times, a chatbot may be sufficient. But if your aim is end-to-end resolution or deeper personalisation, an AI agent is likely the better fit.
- Evaluate your budget: Chatbots are generally more cost-effective to implement and maintain. However, AI agents may offer greater long-term value by reducing escalations and saving time across more complex workflows.
- Decide on your ideal CX: Think about the type of experience you want to deliver. AI in customer experience can take many forms: chatbots offer quick support for predictable needs, whilst AI agents provide more adaptable, personalised interactions for customers requiring more in-depth assistance.
- Weigh data privacy: Since AI agents access more data and systems, ensure your provider prioritises strong privacy protections and responsible AI practices.
Of course, these tools aren’t mutually exclusive. Many businesses combine chatbots and AI agents to deliver flexible support in a balanced approach.
Frequently asked questions
Invest in an industry-leading AI agent with Zendesk
As AI reshapes CX, AI agents and chatbots are becoming indispensable tools for businesses. Leveraging these tools thoughtfully can enable more efficient workflows that keep pace with customer expectations.
Zendesk AI agents provide immediate resolutions around the clock whilst reducing costs at scale. Trained on billions of real customer service interactions, they integrate seamlessly into your support operations and continuously improve based on live data. Learn more about Zendesk AI agents and what they can do for your business.
